Introduction:
Welcome to our blog post on “Designing for the User: A Guide to User-Centered Design Principles”. In today’s digital age, creating user-centered designs has become increasingly important for businesses and organizations. User-centered design principles focus on understanding the needs and preferences of the end-users in order to create meaningful and intuitive experiences.
In this blog post, we will explore the key principles and concepts behind user-centered design and provide practical tips and examples for implementing them. Whether you are a seasoned designer looking to enhance your skills or someone interested in understanding the fundamentals of user-centered design, this guide will provide you with valuable insights to create user-centric designs that delight and engage your target audience.
1. Understanding User-Centered Design
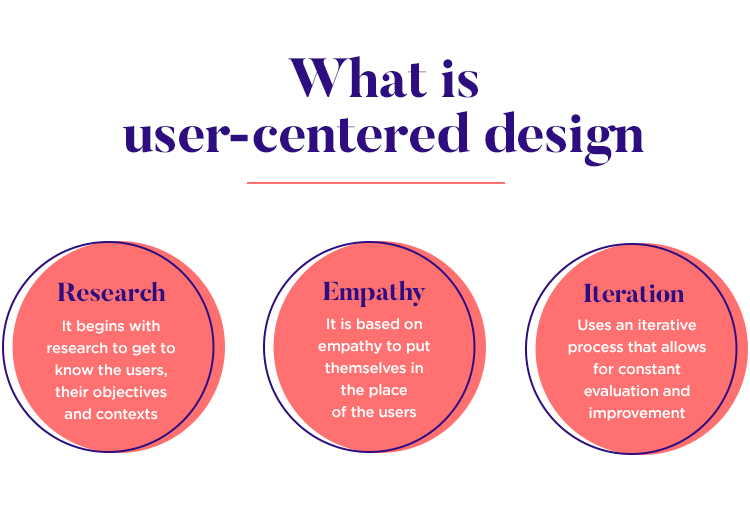
User-Centered Design (UCD) is an approach that prioritizes the needs and preferences of the target audience during the design process. It involves understanding the users, their goals, and creating designs that cater to their expectations.
2. Conducting User Research
Before beginning the design process, it is essential to conduct thorough user research. This includes gathering information about the target audience’s demographics, behavior patterns, and preferences. By understanding users’ needs, designers can create solutions that align with their expectations.
3. Defining User Personas
User personas are fictional characters that represent different user groups. These personas help designers empathize with users and make informed decisions. Creating user personas involves identifying common traits, goals, and challenges of various user segments.
4. User Journey Mapping
User journey mapping allows designers to visualize the user’s experience throughout their interaction with a product or service. It helps identify pain points and areas for improvement. By understanding the user journey, designers can optimize the design to enhance user satisfaction.
5. Creating Intuitive Interfaces
An intuitive interface ensures that users can easily navigate and interact with a product. This involves designing clear and concise menus, logical navigation paths, and intuitive controls. By providing a seamless experience, users can quickly achieve their goals, leading to increased user satisfaction.
6. Prioritizing Accessibility
Designing for accessibility ensures that individuals with disabilities can use a product or service effectively. This includes providing alternative text for images, using color combinations that are accessible for color-blind users, and ensuring keyboard accessibility. Prioritizing accessibility reflects inclusivity and improves overall user experience.
7. Incorporating User Feedback
User feedback is invaluable in improving the design. Feedback can be collected through user testing, surveys, or feedback forms. By actively listening to user suggestions and incorporating them into the design, designers can create user-centered solutions that address user needs and expectations.
8. Iterative Design Process
Iterative design involves continuously refining and improving the design based on user feedback. By testing and iterating, designers can identify and fix usability issues, ensuring that the final product meets user expectations. This iterative approach enhances the user-centered design process.
9. Consistency in Design
Consistency in design elements, such as colors, typography, and layout, enhances user experience. Consistency creates familiarity and allows users to navigate different parts of a product seamlessly. By maintaining a consistent design, users can easily understand and interact with the interface.
10. Continuous User Testing
User testing should be an ongoing process throughout the design lifecycle. Regularly testing the design with actual users helps identify any usability issues and provides insights for improvement. By incorporating user testing into the design process, designers can ensure that the final product meets user needs and expectations.
Summary:

In this blog post, we delve into the world of user-centered design and its significance in today’s digital landscape. User-centered design principles emphasize the importance of understanding users’ needs, preferences, and behaviors to create designs that are intuitive, engaging, and meaningful.
We discuss various key principles and concepts behind user-centered design, including user research, persona development, information architecture, usability testing, and iterative design. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in creating user-centric designs, and we provide practical tips and examples for implementing them effectively.
Whether you are a designer, developer, or business owner, incorporating user-centered design principles into your workflow can have a significant impact on the success of your products or services. By putting the user at the center of the design process, you can create experiences that not only meet users’ needs but also exceed their expectations.
So, join us in this journey of und you can look here erstanding and implementing user-centered design principles, and unlock the power to create designs that truly resonate with your target audience.
- Q: What is user-centered design?
- A: User-centered design is an approach to design that focuses on understanding the needs and preferences of the end user. It involves involving users throughout the design process to create products or services that are intuitive and meet their requirements.
- Q: Why is user-centered design important?
- A: User-centered design is important because it ensures that the final product or service meets the needs and expectations of the users. By involving users in the design process, it reduces the risk of creating something that is difficult to use or doesn’t solve their problems effectively.
- Q: What are the key principles of user-centered design?
- A: The key principles of user-centered design include: understanding the users and their goals, involving users throughout the design process, conducting user research and testing, iterating on designs based on user feedback, and creating intuitive and accessible interfaces.
- Q: How can I understand the needs of the users?
- A: You can understand the needs of the users by conducting user research, such as interviews and surveys, to gather insights about their goals, preferences, and pain points. Observing users in their natural environment and analyzing their behavior and interactions with similar products or services can also provide valuable insights.
- Q: What is the role of prototyping in user-centered design?
- A: Prototyping plays a crucial role in user-centered design as it allows designers to create interactive representations of their ideas and gather feedback from users. It helps to validate design decisions, identify usability issues, and refine the final product or service before investing resources in full-scale development.
- Q: How can I ensure that my design is accessible to all users?
- A: To ensure accessibility, you can follow established guidelines such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). This involves considering factors like color contrast, keyboard navigation, providing alternative text for images, and ensuring compatibility with assistive technologies. Regular usability testing with diverse users can also help identify and address accessibility issues.