Small Scale.That
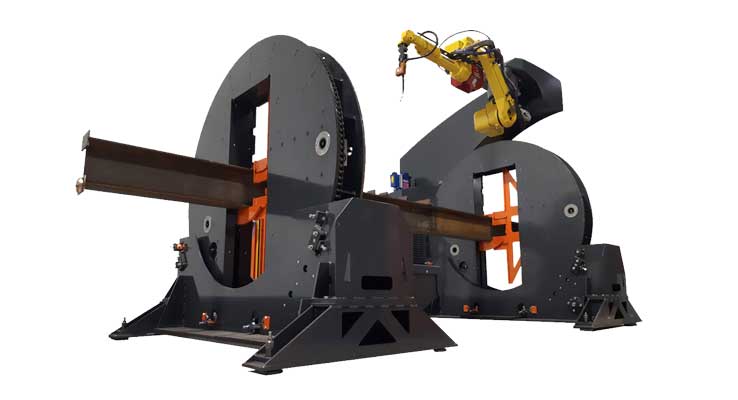
Do you need quality and reliable machines to aid the process of your structural fabrications? We offer structural fabrication machines which will guarantee that only the best beam and plate fabrication outcomes are achieved. These machines include plate processors, beam drill lines, angle masters, thermal cutting machines, layout markers and beam cambering and straightening.